How Do I Register My Ims?
Android 12 introduces support for a single registration model for providing MMTEL and RCS features. This model allows devices to have all IMS features managed through a single IMS registration provided by the device's ImsService and to comply with requirements introduced past some telecom carriers. Compared with a dual registration model, where multiple IMS registrations are managed on 1 device, single registration reduces traffic on the carrier'southward network and increases reliability.
Android 12 supports this unmarried registration model through an architecture with a set of APIs that permit the AOSP telephony stack to manage both MMTEL features provided by ImsService and RCS features provided by the user-selected RCS messaging app. To support IMS unmarried registration, device manufacturers and SoC vendors must implement these APIs to enable RCS features in the user-selected RCS messaging app.
Figure 1 illustrates the device's IMS stack when using the IMS unmarried registration model. All IMS applications apply the device's default ImsService for MMTEL and RCS features over a unmarried IMS registration. This includes provisioning, SIP message forwarding, and RCS user capability exchange.
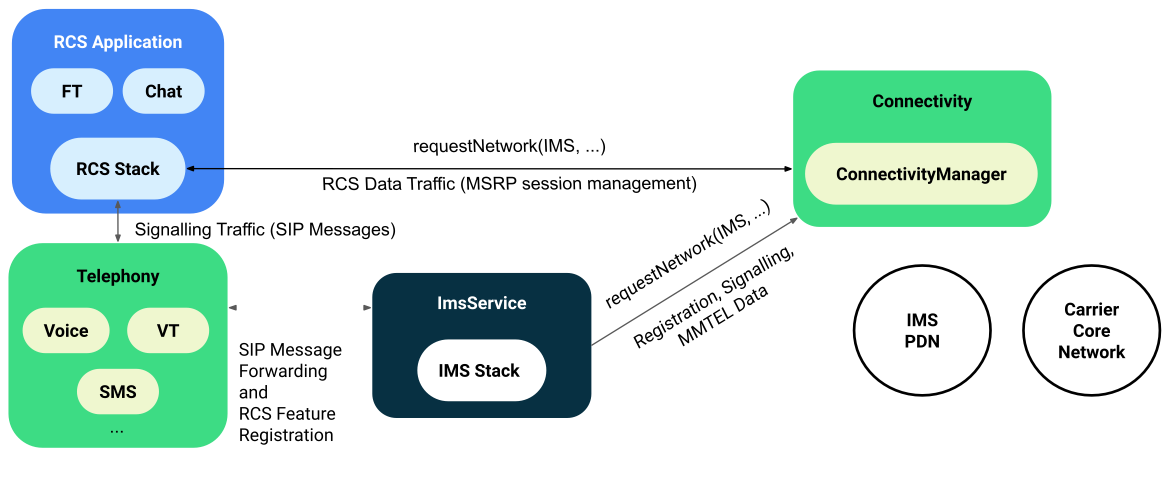
Figure 1. Unmarried registration model compages
Android 11 and lower only supports a dual registration model for providing MMTEL and RCS features, where MMTEL is provided by the device's ImsService and RCS features are implemented over the acme and manage their own IMS stack and connection to the carrier'south network independently.
Figure two illustrates the architecture for the dual registration model. In this model, each app is responsible for connecting to the carrier'southward network and establishing an IMS registration for MMTEL and RCS features. The device's ImsService implements MMTEL, uses the device's IMS data connectedness to the carrier network, and operates independently of other RCS apps.
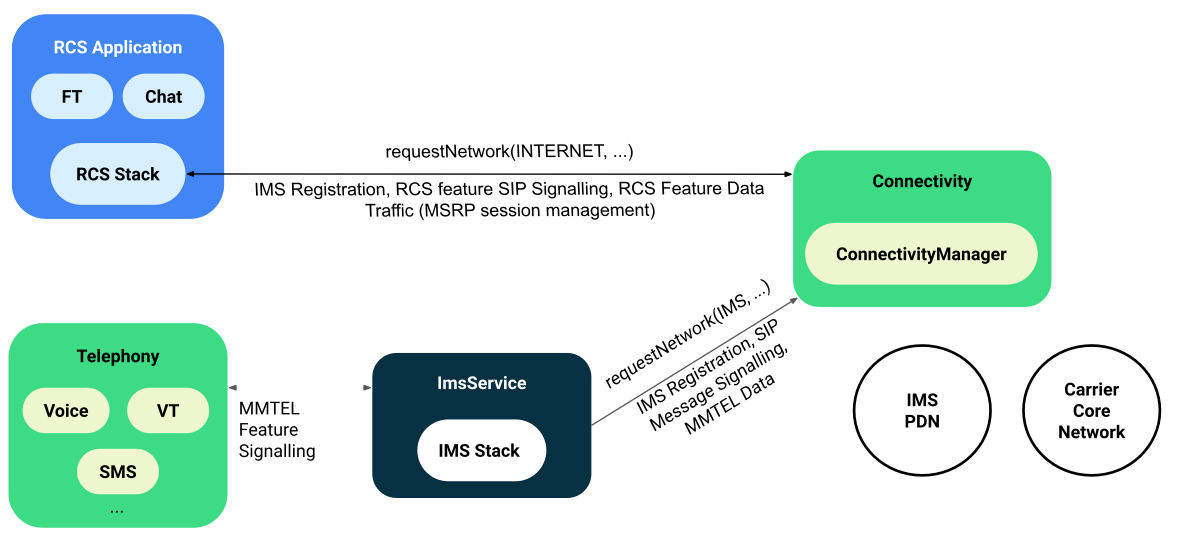
Figure two. Dual registration model compages
IMS single registration APIs
Devices that range on carriers that require IMS unmarried registration must back up the IMS single registration APIs and define the Android characteristic PackageManager#FEATURE_TELEPHONY_IMS_SINGLE_REGISTRATION. Figure 3 shows the APIs that back up IMS unmarried registration.
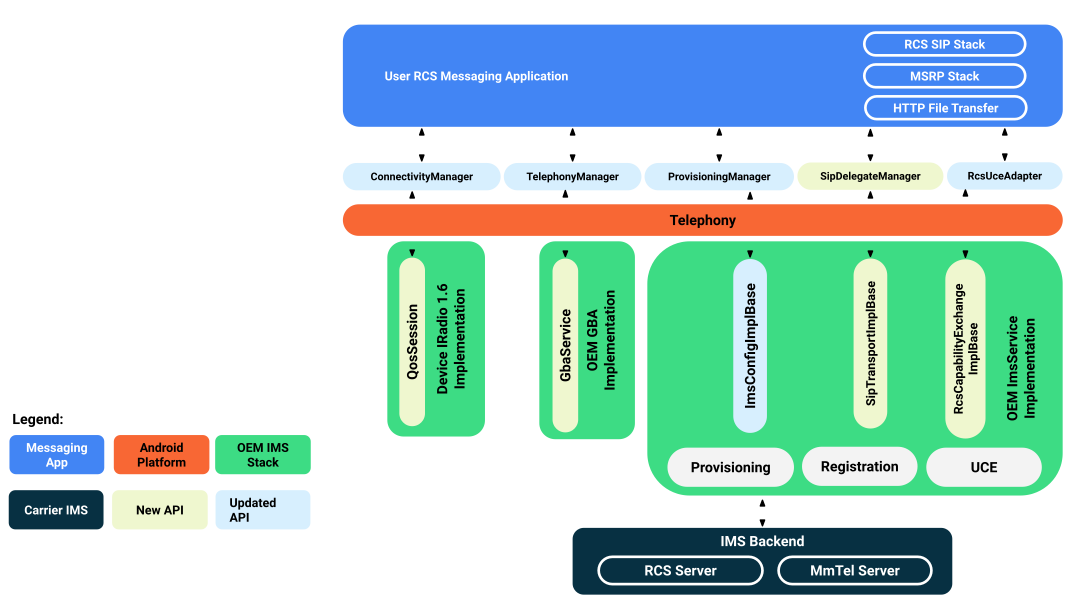
Figure iii. Loftier-level API surfaces that support IMS single registration
Android devices that back up IMS single registration as function of the AOSP telephony stack are required to support all of the AOSP APIs described in the post-obit table.
| API Surface Area | RCS application APIs | Vendor IMS APIs | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCS provisioning | ProvisioningManager | ImsConfigImplBase | Allows an OEM or carrier to provide an app to update the RCS provisioning status if the carrier uses a proprietary carrier entitlement machinery. The ImsService must besides back up the standard AutoConfigurationServer (ACS) for provisioning for carriers that don't employ a proprietary machinery. |
| SIP message forwarding | SipDelegateManager | SipTransportImplBase | Allows an RCS application to beginning associate specific RCS feature tags with the device ImsService, and and so send and receive SIP messages and IMS registration updates associated with those RCS feature tags. |
| Defended bearer notifications | ConnectivityManager | DataCallResponse | Allows an app to heed to QoS notifications on a socket that's associated with a specific local port. |
| GBA authentication | bootstrapAuthenticationRequest | GbaService | Allows an RCS app to authenticate with the network and access keys used for RCS features such as file transfer. |
| RCS user capability exchange | ImsRcsManager | RcsCapabilityExchangeImplBase | Provides AOSP the ability to send its MMTEL and RCS capabilities to the vendor ImsService so that they can be published under one entity to the network for RCS user capability commutation. Also allows other apps interested in the RCS capabilities of one or more contacts to query the network for the contacts RCS capabilities. |
Security and permissions
Android 12 introduces the following permissions to ensure secure access to the carrier's network and user'southward data:
-
android.permission.PERFORM_IMS_SINGLE_REGISTRATION -
android.permission.ACCESS_RCS_USER_CAPABILITY_EXCHANGE
The android.permission.PERFORM_IMS_SINGLE_REGISTRATION permission must be defined by the messaging app with the RCS features. For this permission to be granted, the post-obit must be true:
- The app must be installed as a privileged awarding, meaning that it's preinstalled on the device and is immune to access privileged permissions
- The app must be set up as the user's default SMS office using
RoleManager
If both of these atmospheric condition aren't met, the app is denied access to the android.permission.PERFORM_IMS_SINGLE_REGISTRATION permission. This means that third party apps aren't allowed to access RCS single registration APIs every bit they require carrier certification on the device.
The android.permission.ACCESS_RCS_USER_CAPABILITY_EXCHANGE permission when granted to an app that also has the READ_CONTACTS permission allows the app to request the RCS capabilities of phone numbers using RcsUceAdapter. For this permission to be granted, the following must be true:
- The app must exist installed every bit a privileged application, meaning that it's preinstalled on the device and is allowed to access privileged permissions.
-
The app must be defined every bit one of the post-obit
RoleManagerroles:- Default messaging app: Set past the user.
- Default dialer app: Set by the user.
- Default contacts app: A role introduced in Android 12 that allows the OEM to ascertain a package name through the device overlay value
config_systemContacts, which must stand for to the device's contacts app. That app is so given the contacts function.
To access the IMS APN using ConnectivityManager to set and manage data traffic, apps must too request the android.permission.CONNECTIVITY_USE_RESTRICTED_NETWORKS permission.
Examples and source
Android provides an app in AOSP that implements a test messaging app with basic RCS messaging support for testing and development purposes. You lot tin detect the app at testapps/TestRcsApp. When the app is installed on a device, it can be set every bit the user's default messaging app and will accept the permissions required to access the IMS unmarried registration APIs.
Android besides provides a sample implementation of ImsService for RCS. The source code is at /testapps/ImsTestService.
Implementation
For more implementation details, download IMS Unmarried Registration in Android.
Validation
To validate your implementation of IMS single registration, do the following:
- Ensure the CtsTelephonyTestCases CTS test suite passes.
- Install and run the TestRcsApp to run basic unmarried registration exam cases during integration.
- Pass carrier certification for IMS single registration test cases.
How Do I Register My Ims?,
Source: https://source.android.com/devices/tech/connect/ims-single-registration
Posted by: oconnelltonest.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Do I Register My Ims?"
Post a Comment